AI Governance with RBAC
The AI Administrator for Microsoft 365: Best Practices for IT Professionals
A comprehensive guide to implementing secure AI governance through strategic RBAC controls
Introduction: The Critical Need for AI Governance
As an IT professional, you're witnessing the rapid integration of AI capabilities across Microsoft 365—from Copilot in Teams and SharePoint to AI-powered insights in Viva and Power Platform. While these innovations drive productivity and collaboration, they also introduce new security vectors and governance challenges that traditional administrative roles weren't designed to handle.
The AI Administrator role represents Microsoft's recognition that AI requires specialized governance. However, implementing this role effectively requires more than just another checkbox in your admin center. It demands a strategic approach to role-based access control (RBAC) that balances innovation enablement with security imperatives.
This guide provides practical frameworks for implementing the AI Administrator role while maintaining the security posture that keeps your organization protected and compliant.
Understanding the AI Administrator Role
Core Responsibilities and Permissions
The AI Administrator role sits at the intersection of application management, security governance, and user enablement. Key responsibilities include:
Copilot Agent Management: Approving and publishing line-of-business copilot agents
AI Service Configuration: Managing AI-related enterprise services and extensibility features
Application Oversight: Controlling AI app installations and permissions across the organization
Service Health Monitoring: Accessing Azure and Microsoft 365 AI service dashboards
Usage Analytics: Viewing adoption insights and organizational AI metrics
Support Management: Creating and managing AI-related support tickets
Why Traditional Roles Fall Short
Traditional Microsoft 365 admin roles weren't architected for AI governance. Global Administrators have too much power for routine AI management, while service-specific administrators lack the cross-platform visibility that AI requires. The AI Administrator role fills this gap by providing:
Focused Scope: AI-specific permissions without broad tenant access Cross-Service Visibility: Insight into AI usage across multiple workloads Governance Controls: Approval workflows for AI agent deployment Security Alignment: Integration with existing security and compliance frameworks
RBAC Strategy: Positioning AI Administration
The Privilege Hierarchy
When implementing the AI Administrator role, consider it a High privilege position that requires careful governance:
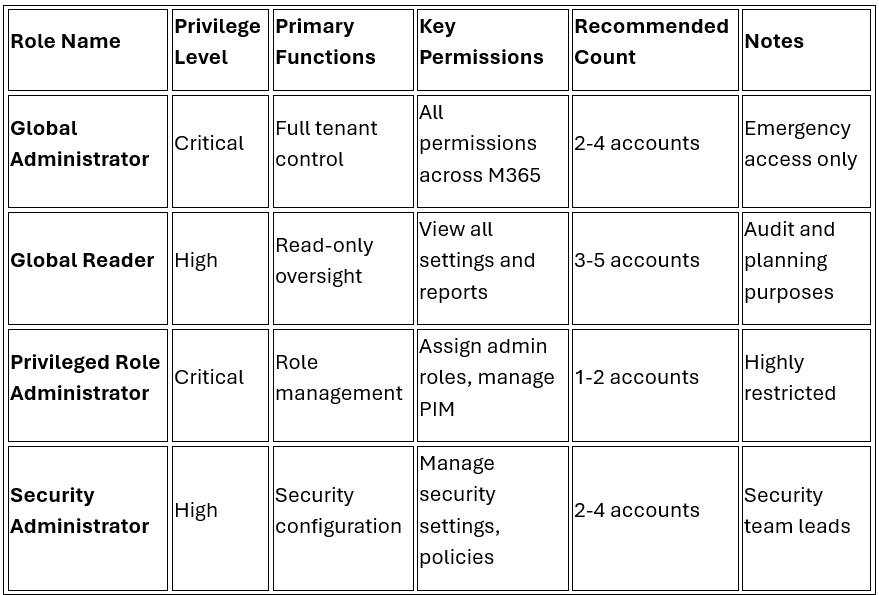
Critical Roles (2-4 accounts)
Global Administrator
Privileged Role Administrator
Security Administrator (lead)
High Privilege Roles (3-8 accounts)
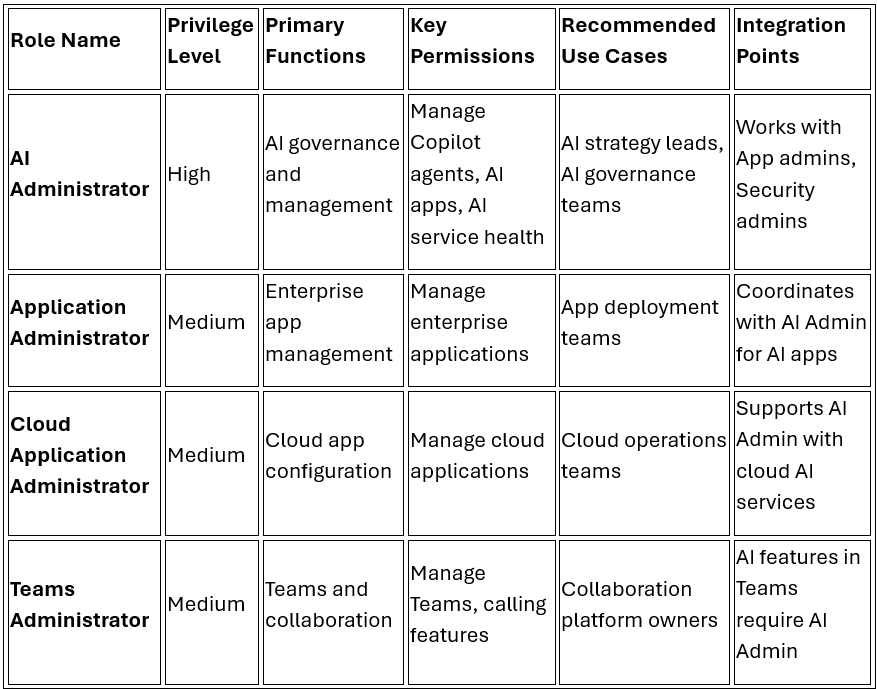
AI Administrator ← Strategic positioning
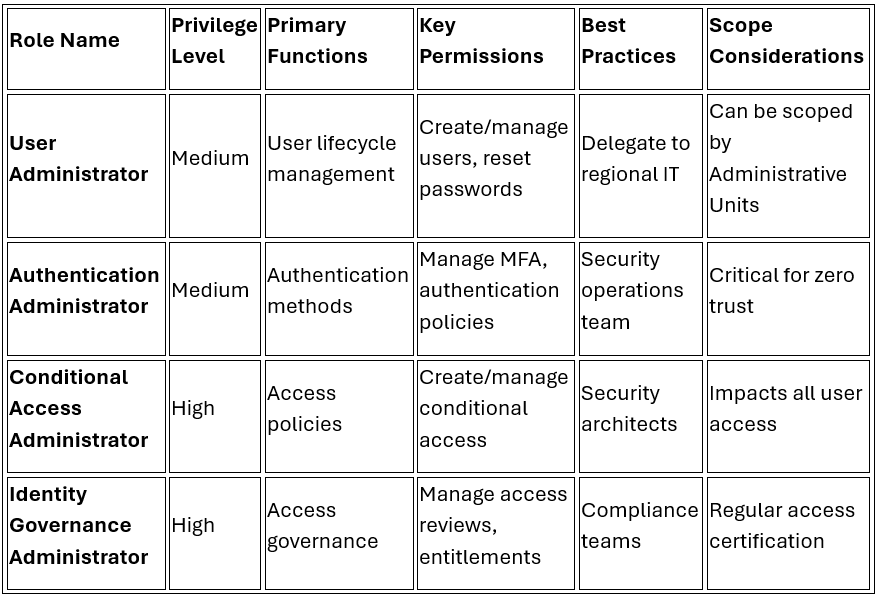
Conditional Access Administrator
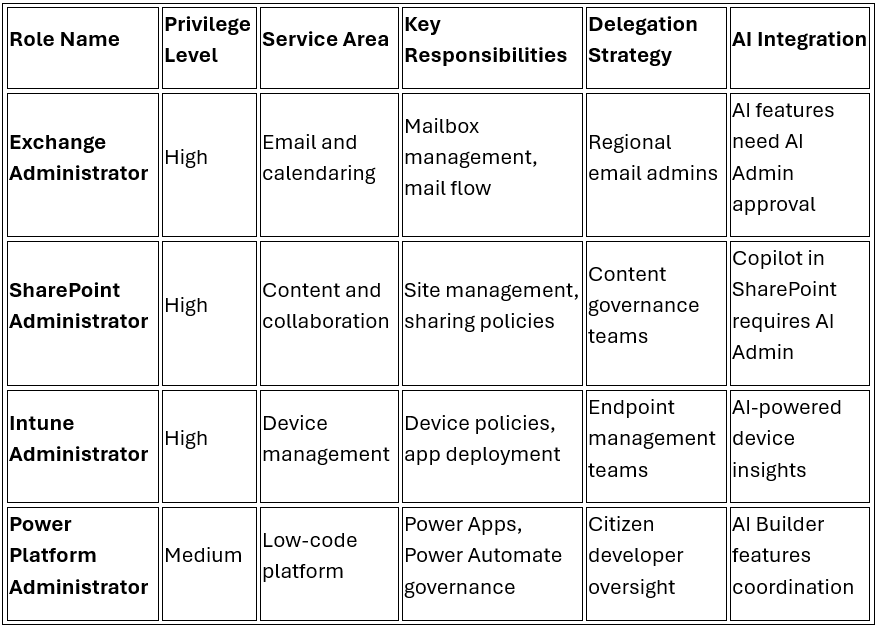
Exchange Administrator
SharePoint Administrator
Medium Privilege Roles (5-15 accounts)
Application Administrator
User Administrator
Teams Administrator
Integration Points
The AI Administrator doesn't operate in isolation. Establish clear coordination protocols with:
Security Administrators: For AI-related security policies and incident response
Application Administrators: For enterprise app management and AI app coordination
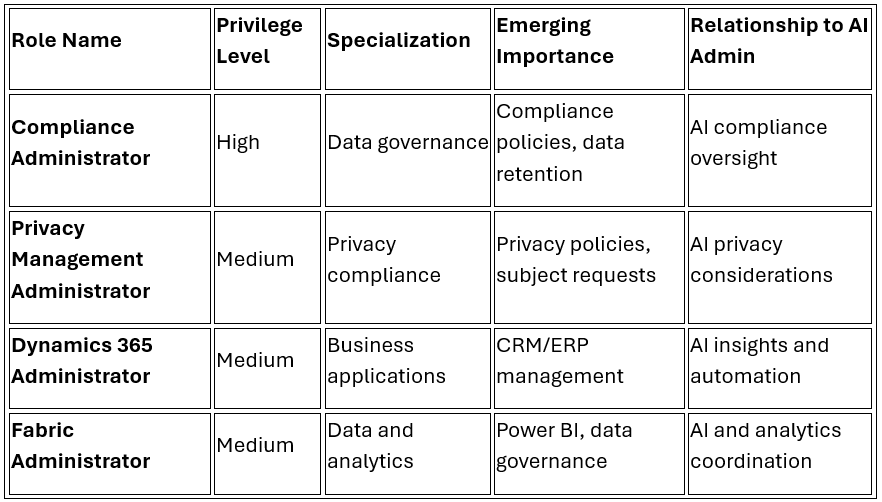
Compliance Administrators: For AI governance and data protection compliance
Service-Specific Admins: For AI feature implementation within their domains
Microsoft 365 RBAC Roles Matrix
Use this comprehensive matrix to understand how the AI Administrator fits into your broader RBAC strategy:
Core Administrative Roles
AI and Modern Workplace Roles
Identity and Access Management
Service-Specific Administrators
Specialized and Emerging Roles
Implementation Best Practices
1. Start with Governance Foundation
Establish AI Governance Policies Before assigning the AI Administrator role, create clear policies around:
AI tool approval processes
Data handling requirements for AI applications
User training and awareness requirements
Incident response procedures for AI-related security events
Create Documentation Standards
Maintain an AI application inventory
Document approval decisions and rationale
Track AI usage metrics and compliance status
Establish change management procedures for AI services
2. Apply Least Privilege Principles
Scope Assignments Carefully
Use Administrative Units to limit AI Administrator scope where possible
Implement time-bound assignments through Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Regular access reviews (quarterly minimum for AI Administrator role)
Just-in-time activation for sensitive AI management tasks
Avoid Over-Privileging
Don't assign Global Administrator rights for AI management
Use custom roles when built-in roles provide too much access
Implement approval workflows for AI app installations
Monitor and audit AI Administrator activities regularly
3. Implement Defense in Depth
Layer Security Controls
Conditional Access policies for AI Administrator accounts
Multi-factor authentication requirements
Privileged workstation requirements for AI administration
Network isolation for administrative activities
Monitor and Alert
Set up alerts for AI app installations and configuration changes
Monitor Copilot agent publishing and approval activities
Track unusual AI service usage patterns
Implement automated response for policy violations
4. Enable Collaboration While Maintaining Control
Cross-Functional Coordination Create regular coordination meetings between:
AI Administrators and Security teams
Business stakeholders and IT governance
Compliance teams and AI strategy leads
End users and support teams
Balanced Enablement
Provide self-service capabilities where appropriate
Implement approval workflows for high-risk changes
Create escalation paths for urgent AI requirements
Maintain communication channels for AI-related questions
Role Assignment Guidelines
Privilege Level Definitions
Critical: Can impact entire tenant, requires emergency procedures
High: Significant impact across multiple services, requires approval workflow
Medium: Service-specific impact, can be delegated with oversight
Low: Limited scope, suitable for front-line support
Assignment Best Practices
Start with least privilege - Assign minimum required permissions
Use time-bound assignments - Leverage PIM for elevated roles
Implement approval workflows - Especially for Critical and High privilege roles
Regular access reviews - Quarterly for Critical, semi-annually for others
Break-glass procedures - Maintain emergency access accounts
AI Administrator Integration Strategy
Position as a High privilege role requiring governance oversight
Coordinate with Application and Security Administrators
Establish approval workflows for AI app deployments
Create escalation paths for AI-related security incidents
Implement regular reviews of AI service usage and compliance
Governance Framework
Role Lifecycle Management
Request Process: Business justification → Security review → Approval
Assignment: Time-bound → Scoped → Monitored
Review Cycle: Regular certification → Usage validation → Renewal/Removal
Incident Response: Rapid revocation → Investigation → Remediation
Monitoring and Compliance
Access logs review: Monthly analysis of admin activities
Privilege escalation tracking: Alert on unusual permission requests
AI governance metrics: Track AI service adoption and compliance
Cross-role coordination: Regular meetings between role holders
Emergency Procedures
Break-glass activation: Clear triggers and approval process
Role escalation: Temporary privilege elevation procedures
Incident response: Rapid role suspension capabilities
Recovery planning: Role restoration after security incidents
Tools and Solutions for Advanced RBAC Management
Native Microsoft Tools
Built-in Role Comparison Use Microsoft's role comparison tool at admin.microsoft.com/AdminPortal/Home#/rbac/directory to understand role overlaps and gaps.
Privileged Identity Management (PIM) Implement PIM for just-in-time access to AI Administrator permissions, reducing standing privileges and improving security posture.
Administrative Units Scope AI Administrator permissions to specific organizational units, geographic regions, or business divisions.
Third-Party Solutions
For organizations requiring advanced RBAC capabilities beyond Microsoft's native tools, consider solutions like CoreView that provide:
Granular Permission Control: Define exactly what AI Administrators can do, eliminating over-privileged access
Virtual Tenant Segmentation: Slice tenants by department, region, or business unit for distributed AI governance
Automated Policy Enforcement: Continuous monitoring and remediation of AI governance policies
Workflow Automation: Streamlined approval processes for AI app deployments and configuration changes
Measuring Success
Key Performance Indicators:
Security Metrics
Reduction in over-privileged accounts (target: <10% of admins with Global Admin)
Time to detect and respond to AI-related security incidents
Compliance with AI governance policies (target: >95%)
Number of AI-related security violations
Operational Metrics
Time to approve and deploy AI applications
User satisfaction with AI service availability
Reduction in help desk tickets related to AI access
AI Administrator workload and efficiency
Governance Metrics
Percentage of AI applications with proper documentation
Regular access review completion rates
AI usage adoption and compliance trends
Stakeholder engagement in AI governance processes
Conclusion: Building Sustainable AI Governance
The AI Administrator role represents a critical evolution in Microsoft 365 administration, but its success depends on thoughtful implementation within a broader RBAC strategy. By following these best practices, you can:
Maintain Security: Implement defense-in-depth controls that protect against AI-related risks
Enable Innovation: Provide streamlined processes that don't impede legitimate AI adoption
Ensure Compliance: Create audit trails and governance processes that meet regulatory requirements
Scale Effectively: Build frameworks that grow with your organization's AI maturity
Remember that AI governance is not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process. Regular reviews, continuous monitoring, and adaptive policies will ensure your RBAC controls remain effective as AI capabilities and threats evolve.
The organizations that successfully balance AI innovation with security will be those that invest in proper governance frameworks today. Start with the fundamentals, build incrementally, and always prioritize security in your AI administration strategy.
For more resources on Microsoft 365 governance and RBAC best practices, consider Microsoft's official documentation and specialized governance platforms that can help automate and scale your AI administration efforts.